
IT SECURITY: THE CHALLENGE IS REAL.

CYBER CRIME IN FULL BLOOM.
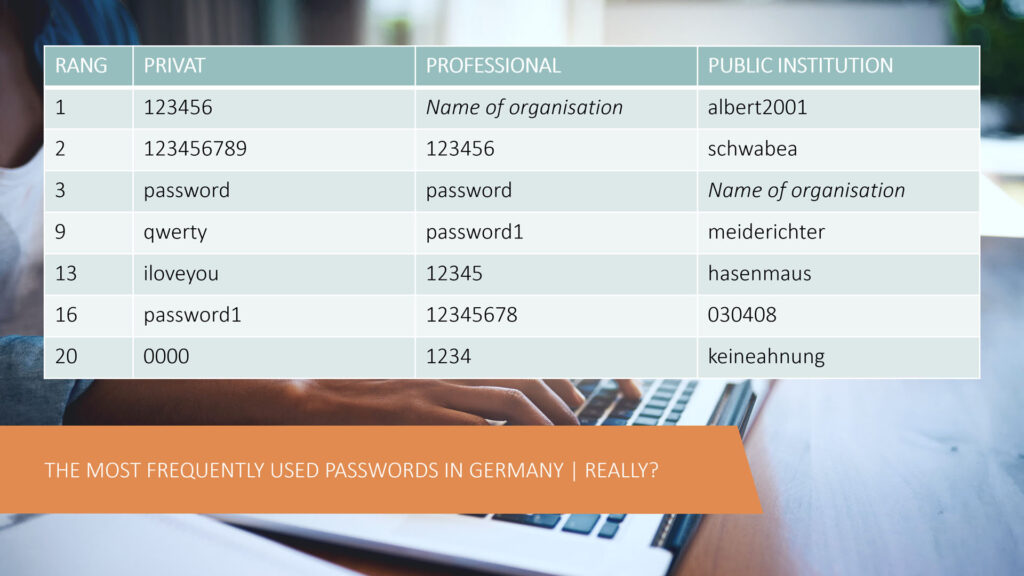
Do you know the most frequently used password in Germany? Correct: It’s still “123456”; in professional contexts people like to use the name of their own organization. While you might smile at this at first, in the face of ever-increasing attack risks, one can really only shake one’s head at it.
In 2023 alone, German companies have suffered losses of around 148 billion euros as a result of cyberattacks. And those are only the known incidents. After all, just because an incident wasn’t noticed, it doesn’t mean that it didn’t occur. No one can answer the question of whether they have ever been affected by an IT security incident with absolute certainty.
So could we call it a heyday of cyber attacks? At the very least, the importance of organized cybercrime is steadily increasing. Organizations of all kinds are now confronted with a highly professionalized cybercrime industry that is up to no good, whether driven by money or political interests. Attack tools and technologies are readily available; the rapid speed of exchange of information additionally makes it possible to consistently exploit security gaps. Thanks to the “cybercrime as a service” business model, those who do not have the necessary expertise themselves can easily acquire the desired attack at a low price.
WHICH ATTACK WAS CHOSEN FOR YOU TODAY?
The fact that the MITRE ATT&CK® database categorizes known attack methods into 234 groups with further subgroups shows just how extensive the range of possible scenarios is – and the trend is rising! The brute force password attack, for example, in which countless passwords are tried for a user name until the correct one is cracked, is widespread. It is particularly effective with weak or frequently used passwords.
Another way to cause damage to companies is to disable a system entirely. With a DDOS attack [Distributed Denial of Service], this can be achieved easily and cheaply. The attack involves generating an excessive number of requests, data, log entries or other processes that put a strain on the IT system’s resources until the system components fail due to overload.
PROFESSIONAL CYBER DEFENSE NEEDED.
Companies today are thus operating in a completely different environment than was the case just a few years ago. That is why it is crucial that the topic of cybersecurity is also increasing in relevance from a regulatory perspective. For example, the NIS2 directive to strengthen cybersecurity is due to come into force across the EU in 2024. It contains a broad catalog of measures relating to risk analysis, dealing with security incidents, managing vulnerabilities, cryptography and much more. In Germany alone, a good 30,000 companies will be covered by the extended level of protection.
But even those who are not affected by NIS2 by definition should see the adopted law as a reminder to improve their security. In the digital era, after all, IT security is not an option, but a necessity. Having a digitalization strategy is inseparable from having a cyber security strategy.

IT SECURITY IS NOT JUST AN IT TASK.
IT security always begins with the definition of a level of protection and the creation of a corresponding framework. Not all applications are equally worthy of protection; critical applications must be prioritized differently than non-critical ones.
An important next step is to consistently integrate security into every project and the entire organization, and even beyond: Security does not stop at system, project or company boundaries. Service providers and project partners must also be involved in order to create a holistic security concept.
Additionally, it should be noted that application landscapes consist of different layers. From the IT infrastructure level to the application base to the functional configuration, they must all be considered in combination when determining a level of protection. Potential attackers will always pick out the weakest point and exploit it for their attack.
This makes clear that IT security is not just an IT task. The responsibility for creating the security concept may lie with the security officer, but all roles in specialist and project areas are responsible for its implementation and compliance.
ADOPTING ZERO TRUST.
Obviously, every company has unique security requirements, so there can be no one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to cybersecurity. However, in adopting the concept of zero trust, there are plenty of best practices that anyone can follow to make their own IT landscape more secure. True to the motto never trust, always verify, it should be assumed that any digital access attempt could be malicious.

LET’S HAVE A LOOK AT PASSWORDS.
It goes without saying that you should not use the password “password1”. But have you ever thought about doing away with passwords altogether? That is one possible password strategy – you can find an overview of others here:
- Use of a second factor: Multiple factor authentication represents an additional barrier and thus ensures that sensitive data is still well protected against unauthorized access, even if a password falls into the wrong hands due to a data leak or phishing.
- Use of an Identity Access Management [IAM]: With the aim of granting only authorized persons and services access to information systems, the main tasks of an IAM are authentication, authorization and user administration. User identities are checked against custom-defined factors and are granted access to resources according to their rights. The level of protection can be further increased, for example, by extending login times and blocking subsequent login attempts.
- Use of passkeys: Passkeys make it possible to log in without any passwords. The user’s device stores a private secret key in its internal memory; at the same time, a matching public key is created and stored on the system in use. To use a passkey, confirmation is required via another security factor, such as a fingerprint.
- Use of Fail2Ban: As an elementary basic component of an effective intrusion prevention system [IPS], Fail2Ban monitors and analyzes the entries in the log files of various services. If anomalies are detected or thresholds are exceeded, such as too many failed log-in attempts, the affected IP addresses are identified and blocked, or other custom mitigation measures are taken. Fail2Ban is therefore an effective measure against brute force attacks.
SOME MORE BEST PRACTICES.
In addition to passwords, there are many effective strategies for securing your digital environments.
- Awareness: Irrespective of technical factors, nothing works without sensitizing employees – as mentioned before, this goes far beyond the IT department. Everyone in the company should take a critical approach to sensitive data and access. This calls for good communication appropriate to the target group; after all, target groups differ within organizations.
- Prediction: In order to be able to recognize risks in advance and communicate them internally, a good picture of your IT situation is required. The BSI reports, for example, are a competent source of information.
- Micro-segmentation: This network security technique divides up networks and segments them into smaller areas, which in turn are provided with their own security controls. If an attack occurs, it is prevented from spreading, and countermeasures can be taken quickly.
- Separation of resources and accounts: If the servers for different services themselves cannot be separated, the services running on one system should be under different user accounts. Rights management should then be used to ensure that a security incident in one account cannot cause any damage to the other user areas. Similar principle: When developing applications, it is also possible to separate areas from one another, for example by using namespaces. If a security incident occurs in one area, the others can still be protected.
- Minimal access rights: In line with the need-to-know principle, access to confidential information is restricted to what is absolutely necessary. This means that users only have access to the information that their roles require at that precise moment.
- Use of the Transport Layer Security [TLS] protocol: The TLS protocol is inserted as a separate layer between the Transmission Control Protocol [TCP] on the communication level and the implementation and display layer protocols of the application in question. It verifies the authenticity of a contacted server via a certificate check and encrypts the connection between client and server. In a further expansion stage in the form of Mutual TLS [mTLS], the identity of the client can also be verified against the server via certificates.
- Web Application Firewall [WAF]: The web application firewall acts as a protective layer between a web application and the internet. All incoming requests and server responses are checked and malicious HTTP/S data traffic or unwanted responses are blocked immediately. Thus, it represents an elementary protection for web applications, which can be run both network-based and host-based.
- Monitoring and alerting: Continuous logging, monitoring and alerting are essential for detecting attacks. Part of vulnerability management, then, is to evaluate detected vulnerabilities immediately. This is where experts come into play in addition to the right technologies.
- Emergency plans: The worst-case scenario cannot always be prevented. In order to ensure the ability to act following a successful attack, concepts such as incident response plans [IRP] and business continuity plans [BCP] should already be in place before the incident occurs. For this, it is helpful to know the critical dependencies of your IT systems.

CONTINUITY IS KEY.
Never touch a running system is the paradigm of the past. Nowadays the rule must be: Frequent updating is queen and king! Security is an ongoing process that is never completed. In order to ensure the long-term protection of applications, it is essential to review the security concept at regular intervals, continuously adapt protection levels and constantly improve the IT security architecture. Regularly installing patches and updates is a necessary part of sustainable IT security. After all, not applying patches means accepting existing vulnerabilities. With regard to the many existing layers of application landscapes, it is important to note that updates must be carried out at each individual level.
Do not forget: Continuous information and monitoring of current market developments is also essential for a consistently effective cyber security strategy.
CONTINUOUS SECURITY IMPROVEMENT BY VIRTIMO.
It is clear that IT security is not a short-distance sprint, but a real marathon. Our top priority is to run this security marathon together with our clients. Starting at the development of our tech stack, through which the topic of security runs like a common thread, to regular updates, we accompany and support our clients at every step of their journey towards a secure IT landscape.
To further secure and improve their application landscapes and solutions, we offer three different packages as part of our security consulting services:
- Security Assessment Package: In the paradigm shift from Trusted Environment to Zero Trust, an intensive review of all existing security facets around Virtimo applications is required. Our experts take a close look at everything from the operating environment to the use of encryption and authentication in the context of business workflows through to their architecture and identify potential for improvement.
- Security Improvement Package: Based on the results of our assessment, we talk you through our recommendations and, either with you or for you, implement appropriate measures to optimize the security of your application. In addition to the topics of clustering, migration and hardening, we place particular focus on your individual processes and applications.
- Security Subscription Package: With the aim of continuously maintaining a high level of security and minimizing effort and cost at the same time, we accompany you on your IT security journey in the long term. This means that we set up extended CVE alerting for your system configuration, proactively inform you about the relevance of updates and assist you with the installation of updates or patches. In addition, a security expert is available to answer any questions, and the assessment of your systems is updated at regular intervals so that we can constantly optimize your security concept.
We also offer you the opportunity to join the Virtimo Defenders’ Club, a forum for exchange on IT security findings and measures.

IT SECURITY: MAIN TAKE-AWAYS.
Phew, as soon as you look closer at the topic of cyber security, you quickly realize that it’s pretty complex. That’s why we’d like to give you our five most important takeaways.
☝️ Cyber crime is real. It’s not a question of if, but when an attack will be attempted.
☝️ Never trust, always verify. Any digital access attempt could be potentially harmful. This is the basis of the Zero Trust security concept.
☝️ IT security is not just an IT task. It must be consistently considered and implemented at all organizational levels in order to be effective.
☝️ There is no all-purpose weapon against cyber attacks. An IT security strategy is only effective when several measures are combined.
☝️ Frequent updating is queen and king! Without a regular review of the security concept and continuous further development of measures and technologies, security is finite.
Would you like a little more input? Here you can find all the presentations from VIRTIMO VISIONS 2024, which focused on IT security, as a video recording. Please note that this event was held in German.

Do you have questions?
I am here for you.

Dirk Breitkreuz
Board Member
Virtimo AG